Differentiating Common Gum Symptoms: Is it Gingivitis, Periodontitis, or Something Else?
Have you ever noticed a tinge of pink in the sink after brushing your teeth? For many, it’s a brief moment of concern, quickly dismissed as the result of brushing too hard. But what if that small sign is your body’s way of sending a crucial message? Understanding the subtle language of your gums is one of the most powerful things you can do for your long-term health, because not all gum symptoms are created equal.
Many people group all gum issues under one umbrella, but the reality is a spectrum, ranging from a simple, reversible warning sign to a serious condition that can impact your entire body. In this guide, we’ll explore the key differences between common gum conditions, helping you decipher what your symptoms might mean and why a professional evaluation is always the best next step.
The Foundation: Understanding the Spectrum of Gum Health
Think of your gum health not as an on/off switch, but as a continuum. At one end, you have healthy, happy gums. At the other, advanced disease. The two most common stages along this path are gingivitis and periodontitis.
What is Gingivitis? The Reversible Warning Sign.
Gingivitis is the earliest and mildest form of gum disease. It’s essentially an inflammation of the gums, caused by the buildup of plaque—a sticky film of bacteria—along the gumline.
Key Symptoms of Gingivitis:
Red, Swollen Gums: Healthy gums are typically pale pink and firm. Inflamed gums look puffy and may appear reddish or purplish.
Bleeding: This is the hallmark sign. Gums may bleed easily during brushing or flossing.
Tenderness: Your gums might feel a bit sensitive, but there's usually no significant pain.
The most important thing to know about gingivitis is that it is completely reversible. The bone and connective tissue holding your teeth in place have not yet been affected. With diligent oral hygiene and professional cleanings, you can restore your gums to full health.
What is Periodontitis? When Inflammation Becomes Destructive.
If gingivitis is left untreated, it can advance to periodontitis. This is where things get serious. In periodontitis, the inflammation spreads below the gumline, and the body's own immune system, in its fight against the bacterial infection, starts to break down the bone and tissues that support the teeth.
Key Symptoms of Periodontitis:
Gums Pulling Away: You might notice your teeth looking longer than they used to. This is gum recession, which creates pockets between the teeth and gums.
Persistent Bad Breath: The bacteria thriving in these pockets can produce unpleasant odours that don't go away with brushing.
Loose or Shifting Teeth: As the supporting bone is lost, teeth can become unstable, leading to changes in your bite.
Pain When Chewing: Sensitivity and discomfort can increase as the condition worsens.
Pus: You may see pus between your teeth and gums, a clear sign of infection.
Unlike gingivitis, the damage caused by periodontitis is irreversible. While treatment can halt the progression of the disease and manage the condition, the lost bone and tissue will not naturally grow back. This is why catching signs early is so critical, as untreated advanced periodontitis is a leading cause of tooth loss in adults.
From Healthy to At-Risk: The Progression of Gum Disease
It’s helpful to visualize the progression as a journey. You don’t just wake up one day with periodontitis. It begins silently, often without any pain, making it easy to ignore the early signs.
Healthy Gums: Firm, pale pink, and fit snugly around the teeth. No bleeding when you brush or floss.
Gingivitis: Plaque buildup irritates the gums, causing inflammation, redness, and bleeding. The damage is still reversible.
Early to Moderate Periodontitis: The gum inflammation worsens, and pockets form. Bone loss begins, but teeth are typically still stable.
Advanced Periodontitis: Significant bone loss occurs, pockets deepen, and teeth may become loose, shift, or even fall out.
Beyond Gingivitis and Periodontitis: What Else Could It Be?
While gingivitis and periodontitis are the most common culprits, other factors can cause similar symptoms. It's important to consider these possibilities, though they all point to the same conclusion: a professional diagnosis is necessary.
Aggressive Brushing: Using a hard-bristled brush or too much force can irritate gums and cause them to bleed or recede.
Hormonal Changes: Fluctuations during pregnancy, puberty, or menopause can make gums more sensitive and prone to swelling and bleeding.
Medication Side Effects: Certain medications, including some for blood pressure or epilepsy, can cause gum overgrowth or dryness, increasing susceptibility to inflammation.
Nutritional Deficiencies: A lack of essential vitamins, particularly Vitamin C, can affect gum health.
Mouth Sores: Canker sores or other oral lesions can cause localized pain and swelling.
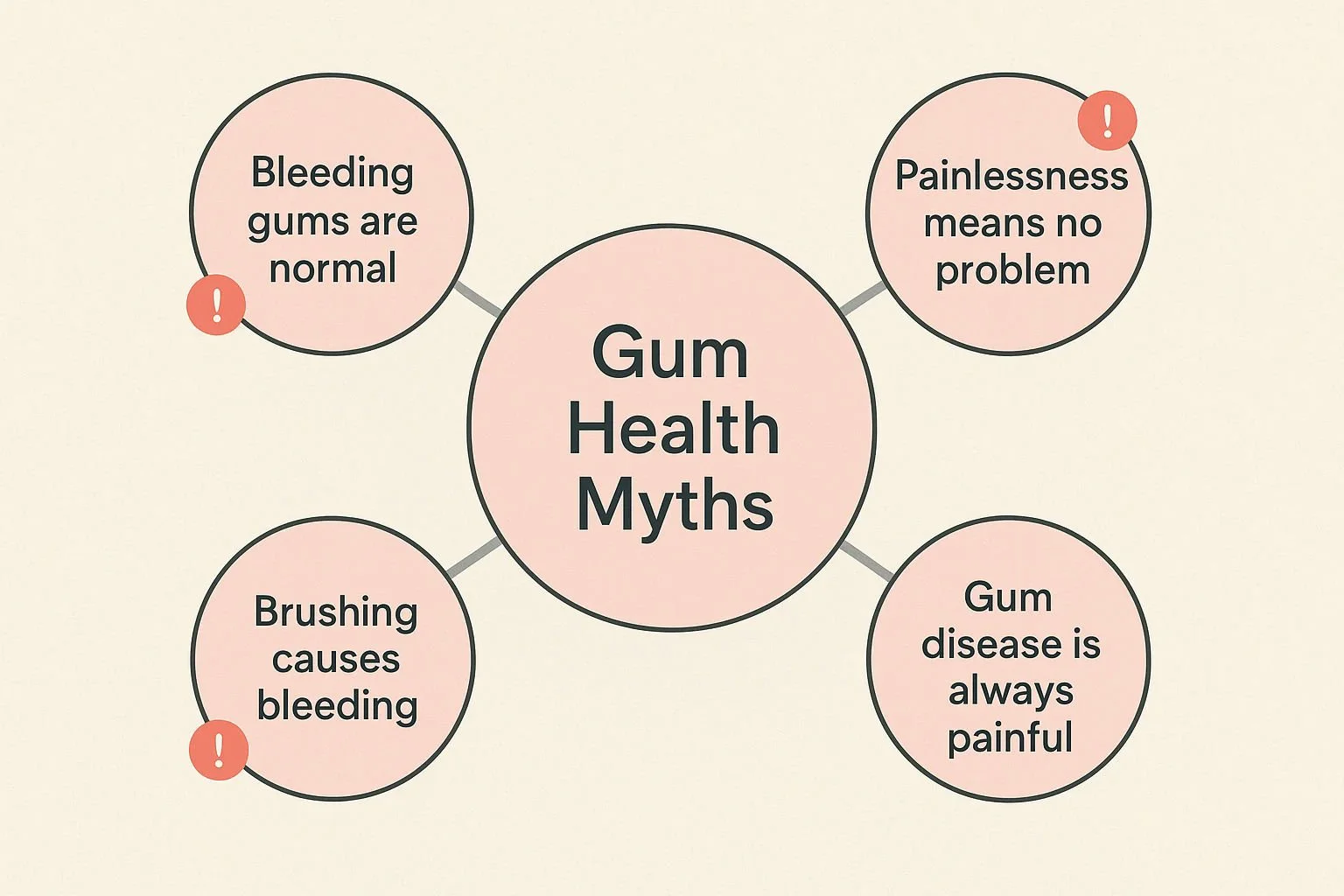
Common Misconceptions: Debunking Myths About Gum Health
There's a lot of misinformation out there about gum health. Let's clear up some of the most common and dangerous myths.
Myth 1: "Bleeding gums are normal, especially if I brush hard."
Fact: This is perhaps the most dangerous myth. Healthy gums do not bleed. Bleeding is your body’s alarm bell for inflammation. While aggressive brushing can cause bleeding, it's far more often an early sign of gingivitis.
Myth 2: "If my gums don't hurt, there's no problem."
Fact: Gingivitis and even early-stage periodontitis are often completely painless. The lack of pain can provide a false sense of security while underlying damage is occurring. Pain is typically a late-stage symptom.
Myth 3: "Gum disease only affects older people."
Fact: While the risk increases with age, gum disease can affect anyone at any age, including children and young adults. According to the CDC, nearly half of adults over 30 have some form of periodontal disease.
Myth 4: "Losing teeth to gum disease is inevitable."
Fact: This is absolutely not true. With early detection, proper care, and modern, non-invasive treatments, the vast majority of teeth can be saved. The key is to address the root cause—the bacterial infection—and halt the disease's progression. Advanced non-invasive options like Duo-Lase™ focus on saving natural teeth by targeting harmful bacteria and stimulating natural healing without traditional surgery.
The Bigger Picture: How Gum Health Impacts Your Whole Body
The bacteria and inflammation associated with periodontitis don't just stay in your mouth. They can enter the bloodstream and travel throughout the body, contributing to or worsening other serious health conditions. Research has established strong links between periodontal disease and:
Heart Disease: The inflammation from gum disease may increase the risk of heart attack and stroke.
Diabetes: The relationship is a two-way street. Periodontitis can make it harder to control blood sugar, and high blood sugar can worsen gum infections.
Respiratory Illnesses: Bacteria from the mouth can be inhaled into the lungs, potentially leading to pneumonia or other respiratory issues.
Pregnancy Complications: Severe gum disease has been linked to premature birth and low birth weight.
Treating your gums isn't just about keeping your teeth; it's about protecting your overall health.
When to See a Dental Professional
Self-diagnosis is never a substitute for professional evaluation. If you experience any of the following symptoms, it's time to schedule an appointment with Behrens Dental Practice:
Gums that bleed consistently when you brush or floss.
Red, swollen, or tender gums.
Gums that have pulled away from your teeth.
Persistent bad breath or a bad taste in your mouth.
Loose teeth or a change in the way your teeth fit together.
Only a dental professional can perform a thorough examination, measure the pockets around your teeth, and determine the true state of your gum health. If you have concerns, seeking guidance from our team of dental professionals at Behrens Dental with a special interest in periodontics is the best way to get a definitive diagnosis and a treatment plan tailored to your specific needs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Can I reverse gum disease on my own?
A1: You can often reverse gingivitis with a strict regimen of brushing twice a day, flossing daily, and attending regular professional cleanings. However, once the disease has progressed to periodontitis, professional intervention is required to manage the condition and prevent further damage.
Q2: How is gum disease diagnosed?
A2: A dentist or dental hygienist will perform a comprehensive periodontal exam. This involves using a small probe to gently measure the depth of the sulcus (the space between your tooth and gum). Healthy pockets are typically 1-3 millimetres deep. Deeper pockets can indicate periodontitis. Sometimes, a microbiological test is also used to identify the specific types of bacteria causing the infection, allowing for a highly targeted treatment plan.
Q3: Are bleeding gums always a sign of gum disease?
A3: While it is the most common sign of gingivitis, it isn't the only cause. Starting a new flossing routine, brushing too aggressively, or certain medications can also cause bleeding. However, because it's such a strong indicator of inflammation, persistent bleeding should never be ignored.
Q4: What's the difference between a regular cleaning and a deep cleaning?
A4: A regular cleaning (prophylaxis) focuses on removing plaque and tartar from the tooth surfaces above the gumline. A deep cleaning (scaling and root planing) is a therapeutic procedure that goes below the gumline to remove tartar buildup from the tooth roots and smooth them out to help the gums reattach.
Your gums are the foundation of your smile. Learning to listen to their signals is the first and most important step in protecting that foundation for life. By understanding the difference between a minor warning and a serious threat, you empower yourself to take action, preserve your natural teeth, and safeguard your overall well-being.